PDF version (NAG web site
, 64-bit version, 64-bit version)
NAG Toolbox: nag_specfun_bessel_i1_real_vector (s18at)
Purpose
nag_specfun_bessel_i1_real_vector (s18at) returns an array of values for the modified Bessel function .
Syntax
Description
nag_specfun_bessel_i1_real_vector (s18at) evaluates an approximation to the modified Bessel function of the first kind for an array of arguments , for .
Note: , so the approximation need only consider .
The function is based on three Chebyshev expansions:
For
,
For
,
For
,
For small
,
. This approximation is used when
is sufficiently small for the result to be correct to
machine precision.
For large , the function must fail because cannot be represented without overflow.
References
Abramowitz M and Stegun I A (1972) Handbook of Mathematical Functions (3rd Edition) Dover Publications
Parameters
Compulsory Input Parameters
- 1:
– double array
-
The argument of the function, for .
Optional Input Parameters
- 1:
– int64int32nag_int scalar
-
Default:
the dimension of the array
x.
, the number of points.
Constraint:
.
Output Parameters
- 1:
– double array
-
, the function values.
- 2:
– int64int32nag_int array
-
contains the error code for
, for
.
- No error.
- is too large. contains the approximate value of at the nearest valid argument. The threshold value is the same as for in nag_specfun_bessel_i1_real (s18af), as defined in the Users' Note for your implementation.
- 3:
– int64int32nag_int scalar
unless the function detects an error (see
Error Indicators and Warnings).
Error Indicators and Warnings
Errors or warnings detected by the function:
Cases prefixed with W are classified as warnings and
do not generate an error of type NAG:error_n. See nag_issue_warnings.
- W
-
On entry, at least one value of
x was invalid.
Check
ivalid for more information.
-
-
Constraint: .
-
An unexpected error has been triggered by this routine. Please
contact
NAG.
-
Your licence key may have expired or may not have been installed correctly.
-
Dynamic memory allocation failed.
Accuracy
Let and be the relative errors in the argument and result respectively.
If
is somewhat larger than the
machine precision (i.e., if
is due to data errors etc.), then
and
are approximately related by:
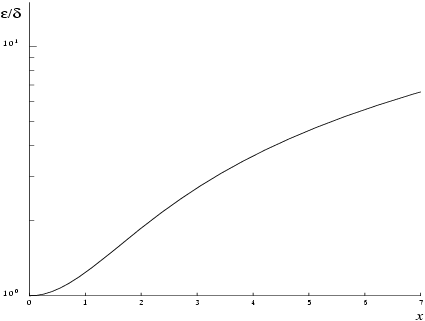
Figure 1 shows the behaviour of the error amplification factor
However, if
is of the same order as
machine precision, then rounding errors could make
slightly larger than the above relation predicts.
For small , and there is no amplification of errors.
For large , and we have strong amplification of errors. However, for quite moderate values of (, the threshold value), the function must fail because would overflow; hence in practice the loss of accuracy for close to is not excessive and the errors will be dominated by those of the standard function exp.
Further Comments
None.
Example
This example reads values of
x from a file, evaluates the function at each value of
and prints the results.
Open in the MATLAB editor:
s18at_example
function s18at_example
fprintf('s18at example results\n\n');
x = [0; 0.5; 1; 3; 6; 8; 10; 15; 20; -1];
[f, ivalid, ifail] = s18at(x);
fprintf(' x I_1(x) ivalid\n');
for i=1:numel(x)
fprintf('%12.3e%12.3e%5d\n', x(i), f(i), ivalid(i));
end
s18at example results
x I_1(x) ivalid
0.000e+00 0.000e+00 0
5.000e-01 2.579e-01 0
1.000e+00 5.652e-01 0
3.000e+00 3.953e+00 0
6.000e+00 6.134e+01 0
8.000e+00 3.999e+02 0
1.000e+01 2.671e+03 0
1.500e+01 3.281e+05 0
2.000e+01 4.245e+07 0
-1.000e+00 -5.652e-01 0
PDF version (NAG web site
, 64-bit version, 64-bit version)
© The Numerical Algorithms Group Ltd, Oxford, UK. 2009–2015